
Hydrogen peroxide
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
 المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
 الجزء والصفحة:
ص406-407
الجزء والصفحة:
ص406-407
 2025-09-10
2025-09-10
 383
383
Hydrogen peroxide
Key point: Hydrogen peroxide is susceptible to decomposition by disproportionation at elevated temperatures or in the presence of catalysts. Hydrogen peroxide is a very pale blue, viscous liquid. It has a higher boiling point than water (150C) and a greater density (1.445 g cm3 at 25C). It is miscible in water and is usually handled in aqueous solution. The Frost diagram for oxygen (Fig. 16.2) shows that H2O2 is a good oxidizing agent, but it is unstable with respect to disproportionation:
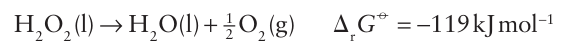
This reaction is slow but is explosive when catalysed by a metal surface or alkali dissolved from glass. For this reason, hydrogen peroxide and its solutions are stored in plastic bottles and a stabilizer is added. This reaction can be considered in terms of the reduction half-reactions
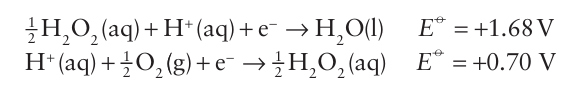
Any substance with a standard potential in the range 0.70 1.68 V that has suitable binding sites will catalyse this reaction. As can be inferred from these standard potentials, hydrogen peroxide is a very powerful oxidizing agent in acid solution:
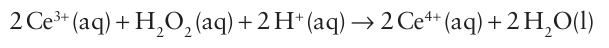
However, in basic solution hydrogen peroxide can act as a reducing agent:
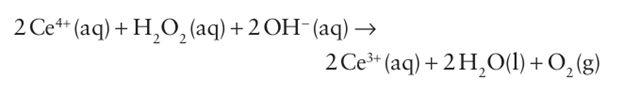
The underlying reason for the oxidizing nature of hydrogen peroxide lies in the weakness of the O-O single bond (146 kJ mol 1). Hydrogen peroxide reacts with d-metal ions such as Fe2+ to form the hydroxyl radical in the Fenton reaction:
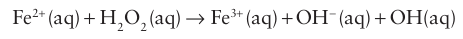
The Fe3+ product can react with a second H2O2 to regenerate Fe2+ , so that the production of hydroxyl radical is catalytic. The O hydroxyl radical is one of the strongest oxidizing agents known (E ْ=+2.85 V) and the reaction is used to oxidize organic mat ter. In living cells, its reaction with DNA has potentially lethal consequences.

Hydrogen peroxide is a slightly stronger acid than water:
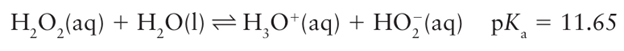
Deprotonation occurs in other basic solvents such as liquid ammonia, and NH4OOH has been isolated and found to consist of NH4 and HO2 ions. When solid NH4OOH melts (at 25C), the melt contains hydrogen-bonded NH3 and H2O2 molecules. The oxidizing ability of hydrogen peroxide and the harmless nature of its byproducts lead to its many applications. It is used in water treatment to oxidize pollutants, as a mild antiseptic, and as a bleach in the textile, paper, and hair-care industries (Box 16.2).
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


