
Boron clusters
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
 المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
 الجزء والصفحة:
ص329-330
الجزء والصفحة:
ص329-330
 2025-08-31
2025-08-31
 316
316
Boron clusters
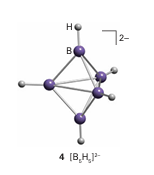
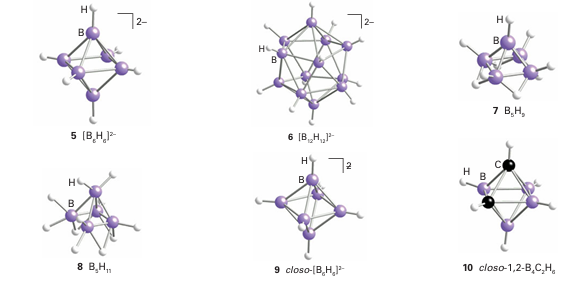
Key point: Boron forms an extensive range of polymeric, cage-like compounds which include the boro hydrides, metallaboranes, and the carboranes. In addition to the simple hydrides, B forms several series of neutral and anionic polymeric cage-like boron hydrogen compounds. Borohydrides are formed with up to 12 B atoms and fall into three classes called closo, nido, and arachno. The borohydrides with the formula [BnHn]-2 have a closo structure, a name derived from the Greek for ‘cage’. This series of anions is known for n = 5 to 12, and examples include the trigonal-bipyramidal [B5H5]-2 ion (4), the octahedral [B6H6 ]-2 ion (5), and the icosa hedral [B12H12]-2 ion (6). When boron clusters have the formula BnHn+4 they adopt the nido structure, a name derived from the Latin for ‘nest’. An example is B5H9 (7). Clusters of formula Bn Hn 6 have an arachno structure, from the Greek for ‘spider’ (as they resemble untidy spiders’ webs). One example is pentaborane (11) (B5H11, 8). Boron forms many metal-containing clusters called the metallaboranes. In some cases, the metal is attached to a borohydride ion through hydrogen bridges. A more common and generally more robust group of metallaboranes have direct M B bonds. Closely related to the polyhedral boranes and borohydrides are the carboranes (more formally, the carbaboranes), a large family of clusters that contain both B and C atoms. An analogue of B6H6-2 (9) is the neutral carborane B4C2H6 (10).
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


