
Superacids and superbases
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
 المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
 الجزء والصفحة:
142-143
الجزء والصفحة:
142-143
 2025-08-28
2025-08-28
 513
513
Superacids and superbases
Key point: Superacids are more efficient proton donors than anhydrous sulfuric acid. Superbases are more efficient proton acceptors than the hydroxide ion. A superacid is a substance that is a more efficient proton donor than pure H2SO4. Superacids are typically viscous, corrosive liquids and can be up to 1018 times more acidic than H2SO4 itself. They are formed when a powerful Lewis acid is dissolved in a powerful Brønsted acid. The most common superacids are formed when SbF5 is dissolved in fluorosulfonic acid, HSO3 F, or anhydrous HF. An equimolar mixture of SbF5 and HSO3 F is known as ‘magic acid’, so named because of its ability to dissolve candle wax. The enhanced acidity is due to the formation of a solvated proton, which is a better proton donor than the acid:
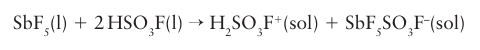
An even stronger superacid is formed when SbF5 is added to anhydrous HF:
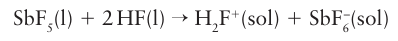
Other pentafluorides also form superacids in HSO3 F and HF and the acidity of these com pounds decreases in the order SbF5 > AsF5 > TaF5 > NbF5 > PF5. Superacids are known that can protonate almost any organic compound. In the 1960s, George Olah and his colleagues found that carbonium ions were stabilized when hydro carbons were dissolved in superacids.7 In inorganic chemistry, superacids have been used to observe a wide variety of reactive cations such as S82+, H3O2+, Xe2+, and HCO+, some of which have been isolated for structural characterization.
A superbase is a compound that is a more efficient proton acceptor than the OH– ion, the strongest base that can exist in aqueous solution. Superbases react with water to produce the OH– ion. Inorganic superbases are usually salts of Group 1 or Group 2 cations with small, highly charged anions. The highly charged anions are attracted to acid solvents such as water and ammonia. For example, lithium nitride, Li3 N, reacwts violently with water:
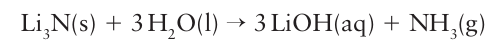
The nitride anion is a stronger base than the hydride ion and deprotonates hydrogen:
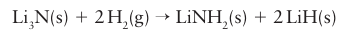
Lithium nitride is a possible hydrogen storage material as this reaction is reversible at 270°C (Box 10.4). Sodium hydride is a superbase that is used in organic chemistry to deprotonate carboxylic acids, alcohols, phenols, and thiols. Calcium hydride reacts with water to liberate hydrogen:
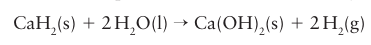
Calcium hydride is used as a dessicant, to inflate weather balloons, and as a laboratory source of pure hydrogen.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


