
Lewis acids and bases of the s-block elements
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
 المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
 الجزء والصفحة:
133
الجزء والصفحة:
133
 2025-08-27
2025-08-27
 402
402
Lewis acids and bases of the s-block elements
Key point: Alkali metal ions act as Lewis acids with water, forming hydrated ions. The existence of hydrated alkali metal ions in water can be regarded as an aspect of their Lewis acid character, with H2O the Lewis base. Alkali metal ions do not act as Lewis bases but their fluorides act as a source of the Lewis base F– and form fluoride complexes with Lewis acids, such as SF4:
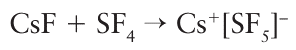
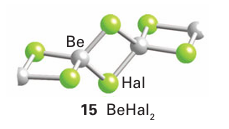
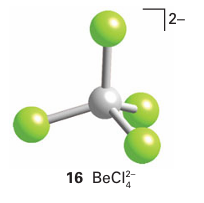
The Be atom in beryllium dihalides acts as a Lewis acid by forming a polymeric chain structure in the solid state (15). In this structure, a Ϭ bond is formed when a lone pair of electrons of a halide ion, acting as a Lewis base, is donated into an empty sp3 hybrid orbital on the Be atom. The Lewis acidity of beryllium chloride is also demonstrated by the forma tion of adducts such as BeCl4-2 (16).
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


