

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences

Clauses

Part of Speech


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Language shift in early modern Ireland
المؤلف:
Raymond Hickey
المصدر:
A Handbook Of Varieties Of English Phonology
الجزء والصفحة:
70-4
2024-02-16
1548
Language shift in early modern Ireland
Literary parodies do not reveal anything about the then relationship of Irish to English, the spread of English and the regional input from England. There were no censuses before 1851 which gave data on speakers of Irish and English. Adams (1965) is a useful attempt to nonetheless produce a linguistic cartography of Ireland at the beginning of the early modern period. The upshot of this situation is that there is no reliable data on the language shift which began in earnest in the early 17th century and which had been all but completed by the late 19th century.
It is clear that the Irish learned English from other Irish who already knew some, perhaps through contact with those urban Irish who were English speakers, especially on the east coast and through contact with the English planters and their employees. This fact had consequences for the nature of Irish English. Bliss (1977) pointed out that this fact is responsible for both the common malapropisms and the unconventional word stress found in Irish English. However, the stress pattern in verbs with final long vowels, e.g. distribute 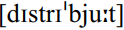 , educate [edjuIke:t] , can also be due to English input, particularly as late stress is a feature of southern Irish, not of the west and north, and so influence due to contact with Irish could only be posited for the south of Ireland.
, educate [edjuIke:t] , can also be due to English input, particularly as late stress is a feature of southern Irish, not of the west and north, and so influence due to contact with Irish could only be posited for the south of Ireland.
Another point concerning the language shift in Ireland is that it was relatively long, spanning at least three centuries from 1600 to 1900 for most of the country. The scenario for language shift is one where lexical transfer into English is unlikely, or at least unlikely to become established in any nascent supraregional variety of English in Ireland. Such dictionaries as Ó Muirithe (1996) and to a lesser extent Dolan (1998) seem to reveal a large number of Irish loans in present-day Irish English. But the question of currency is the key issue here: there is a great difference between the vocabulary of an older agricultural generation (which is frequently reflected in the entries in these dictionaries) and a younger urban one.
In phonology and syntax the matter is quite different. Speakers who learn a language as adults retain the pronunciation of their native language and have difficulty with segments which are unknown to them. A simple case of this would be the substitution of English dental fricatives by stops (dental or sometimes alveolar, depending on region) in Irish English. A more subtle case would be the lenition of stops in Irish English, e.g. cat [kæt], which, while systemically completely different from lenition in Irish, could be the result of a phonological directive applied by the Irish learning English to lenite elements in positions of maximal sonority.
 الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















