
Lipids
 المؤلف:
Karp, G
المؤلف:
Karp, G
 المصدر:
Cell and Molecular Biology
المصدر:
Cell and Molecular Biology
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 22-10-2015
22-10-2015
 2612
2612
Lipids
Lipids are uniquely biological molecules, and they are synthesized and used by organisms in a variety of important ways. Unlike proteins, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids, lipids are much smaller, water-insoluble molecules. They are synthesized in association with a cellular organelle called the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. In a word, they are, as their etymology suggests, fats.
Several types of fats are made from fatty acids. Fatty acids are long, unbranched chains of hydrocarbons (typically made up of fourteen to twenty carbons) with a terminal organic acid group. In cartoon figures, fatty acids are often drawn as lollypops, consisting of long hydrocarbon “tails” and circular, polar “heads.” When free in cells, the acidic heads give the fatty acids a negative charge, which is lost when the molecules are linked chemically with glycerol to form glycerides.
Possibly the most common fat is a glyceride, which consists of fatty acids linked to glycerol (a three-carbon alcohol). Triglycerides are the most prevalent glyceride; they each contain three fatty acids, and because they are used almost exclusively for the storage of biological energy, they are the most common component of body fat. To understand their storage function it is useful to appreciate that the fatty acids commonly found in triglycerides each contain more than twice the energy present in octane, the primary component of gasoline.
Diglycerides are also common lipids; they are especially abundant in biological membranes (unlike triglycerides, which are never found in membranes). As its name suggests, a diglyceride contains two fatty acids linked to a glycerol backbone; the third carbon of glycerol is usually linked to a much more polar substance. The most common diglycerides found in membranes are phospholipids, compounds whose polar groups consist of negatively charged phosphate groups linked to other polar compounds (such as the organic base choline, or the amino acid serine, or the simple sugar inositol).
Unlike triglycerides, most diglycerides are distinctly “schizophrenic” (or more technically, amphipathic) with respect to their solubility properties. The fatty acid residues are distinctly hydrophobic, whereas the polar residue is very hydrophilic. Thus, the polar part of a phospholipid wants to dissolve in aqueous solutions, while the nonpolar parts prefer their own company, so to speak. This amphipathic property is the basis for the spontaneous assembly of phospholipids into bilayer membranes and for the dynamic stability these important cellular components exhibit. For this reason phospholipid and other amphipathic membrane lipids are often called “structural lipids.”
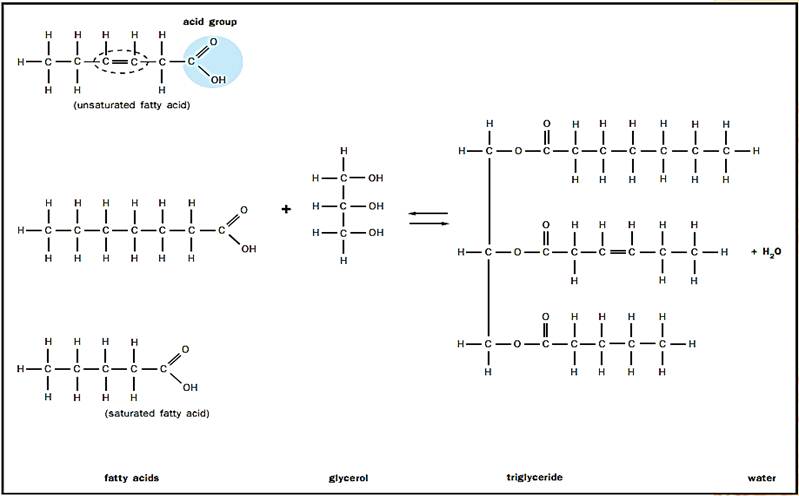
Fatty acids link to glycerol, by removal of water molecules, to make a triglyceride. If a phosphate group (PO43-) is used instead of one of the fatty acids, a phospholipid is formed. The phosphate end dissolves in water, while the fatty acid end does not.
Other structural, amphipathic lipids include glycolipids with polar residues consisting of one or more carbohydrates and hydrophobic regions containing both hydrocarbon and fatty acid residues, and cholesterol, a complex cyclical hydrocarbon with a very small polar residue. Cholesterol is also the parent compound of a group of very important hormones called steroids (including cortisol, estrogen, progesterone, and androgen) and of bile salts that facilitate the digestion of dietary fats.
In some organisms, fatty acids may also be linked to long-chain hydrocarbon alcohols, producing compounds called waxes; the spermaceti of sperm whales and the substances used by bees to form the walls of their honeycomb are good examples. Also uncommon, but very important in some plants, are hydrocarbons called terpenes, of which turpentine and camphor are the most well-known examples, and carotenoids, a yellow plant pigment.
References
Karp, G. Cell and Molecular Biology, 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2001.
 الاكثر قراءة في الأحياء العامة
الاكثر قراءة في الأحياء العامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


