
Cytokinesis
 المؤلف:
Alberts, Bruce
المؤلف:
Alberts, Bruce
 المصدر:
The Molecular Biology of the Cell
المصدر:
The Molecular Biology of the Cell
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 14-10-2015
14-10-2015
 2861
2861
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process by which a cell divides its cytoplasm to produce two daughter cells. As the final step in cell division after mitosis, cytokinesis is a carefully orchestrated process that signals the start of a new cellular generation. The separation of one cell into two is accomplished by a structure called the contractile ring. The contractile ring is a structure believed to operate in a way similar to muscle. A molecular motor, myosin, contracts the actin filaments that form the contractile ring tighter and tighter until the cell is pinched in two. The contraction of the contractile ring has been likened to tightening a purse string to close the top of a pouch. The furrow created by this pinching process is also called the “cleavage furrow,” as it is the site at which cleavage of one cell into two cells occurs.
Cytokinesis consists of four major steps. The first step is to define the position at which the contractile ring will form. The spindle, the structure responsible for segregating the chromosomes into what will become the daughter cells, also appears to be responsible for defining where the contractile ring forms. The contractile ring forms perpendicular to the long axis of the spindle at its midpoint. Components of the spindle that come in contact with the plasma membrane, called astral microtubules, are believed to transmit a signal to the cell periphery that tells actin and other components of the contractile ring to assemble at that location. Actin and microtubules are both part of the cytoskeleton.
The second step in cytokinesis is to assemble the actin filaments that form the contractile ring. Additional proteins, including the molecular motor myosin, which powers contraction, also assemble in this same domain. The third step is the actual contraction of the contractile ring. In this step, the myosin motor, powered by adenosine triphosphate, moves the actin filaments past each other, much in the same way as myosin interacts with actin to power the contraction of muscle. This step also requires the removal of actin subunits to allow the ring to decrease in size. The final step, breaking and refusion of the plasma membrane, occurs once the ring has contracted to its minimum size. This breaking and fusion finally separates the two daughter cells from each other.
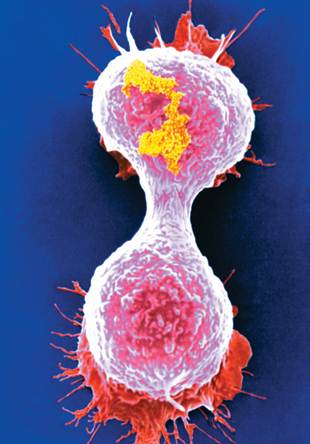
A colored scanning electron micrograph of a breast cancer cell dividing.
As with each of the steps in mitosis, cytokinesis is highly regulated. If the cell were to divide its cytoplasm prior to the completion of duplication and segregation of the chromosomes, it is unlikely that each of the progeny cells would receive the proper genetic information. Thus the cell employs several regulatory mechanisms to assure that cytokinesis occurs only after all of the chromosomes have been properly segregated. There is, for example, a “spindle checkpoint” that assures that each and every chromosome has attached to the spindle. The entire process of cell division waits at the checkpoint until the conditions of the checkpoint have been satisfied. Once they have been, the process continues and concludes with cytokinesis.
References
Alberts, Bruce, et al. The Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed. New York: Garland Publishing, 2000.
Bray, Dennis. Cell Movements. New York: Garland Press, 1992.
Lodish, Harvey, et al. Molecular Cell Biology, 3rd ed. New York: Scientific American Books, 1995.
 الاكثر قراءة في الأحياء العامة
الاكثر قراءة في الأحياء العامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


