

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Close-Packing of Identical Spheres
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
2-5-2020
1451
Close-Packing of Identical Spheres

The essential difference here is that any marble within the interior of the square-packed array is in contact with four other marbles, while this number rises to six in the hexagonal-packed arrangement. It should also be apparent that the latter scheme covers a smaller area (contains less empty space) and is therefore a more efficient packing arrangement. If you are good at geometry, you can show that square packing covers 78 percent of the area, while hexagonal packing yields 91 percent coverage.
If we go from the world of marbles to that of atoms, which kind of packing would the atoms of a given element prefer?
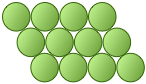
If the atoms are identical and are bound together mainly by dispersion forces which are completely non-directional, they will favor a structure in which as many atoms can be in direct contact as possible. This will, of course, be the hexagonal arrangement.
Directed chemical bonds between atoms have a major effect on the packing. The version of hexagonal packing shown at the right occurs in the form of carbon known as graphite which forms 2-dimensional sheets. Each carbon atom within a sheet is bonded to three other carbon atoms. The result is just the basic hexagonal structure with some atoms missing.
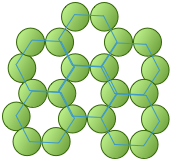
The coordination number of 3 reflects the sp2-hybridization of carbon in graphite, resulting in plane-trigonal bonding and thus the sheet structure. Adjacent sheets are bound by weak dispersion forces, allowing the sheets to slip over one another and giving rise to the lubricating and flaking properties of graphite.
 الاكثر قراءة في اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















