

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Names and Physical Properties of Cycloalkanes
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
26-1-2020
2011
Names and Physical Properties of Cycloalkanes
Many organic compounds found in nature contain rings of carbon atoms. These compounds are known as cycloalkanes. Cycloalkanes have one or more rings of carbon atoms. Cycloalkanes only contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and carbon-carbon single bonds. The simplest examples of this class consist of a single, un-substituted carbon ring, and these form a homologous series similar to the unbranched alkanes.
Like alkanes, cycloalkane molecules are often drawn as skeletal structures in which each intersection between two lines is assumed to have a carbon atom with its corresponding number of hydrogens. Cyclohexane, one of the most common cycloalkanes is shown below as an example.
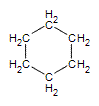.gif?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=85&height=92) same as
same as 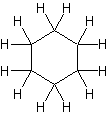 same as
same as 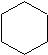
Cyclic hydrocarbons have the prefix "cyclo-". The IUPAC names, molecular formulas, and skeleton structures of the first ten cycloalkanes are given in Table 1.1. Note that the general formula for a cycloalkane composed of n carbons is CnH2n, and not CnH2n+2 as for alkanes. Although a cycloalkane has two fewer hydrogens than the equivalent alkane, each carbon is bonded to four other atoms so are still considered to be saturated with hydrogen.
| Table 1.1: Examples of Simple Cycloalkanes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cycloalkane | Molecular Formula | Skeleton Structure |
| Cyclopropane | C3H6 | 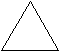 |
| Cyclobutane | C4H8 |  |
| Cyclopentane | C5H10 | 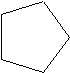 |
| Cyclohexane | C6H12 | 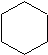 |
| Cycloheptane | C7H14 | 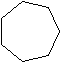 |
| Cyclooctane | C8H16 | 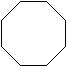 |
| Cyclononane | C9H18 | 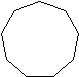 |
| Cyclodecane | C10H20 | 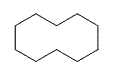 |
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















