

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Deriving the Ideal Gas Law
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
13-6-2019
1839
Deriving the Ideal Gas Law
Any set of relationships between a single quantity (such as V) and several other variables (P , T, and n) can be combined into a single expression that describes all the relationships simultaneously. The three individual expressions were derived previously:
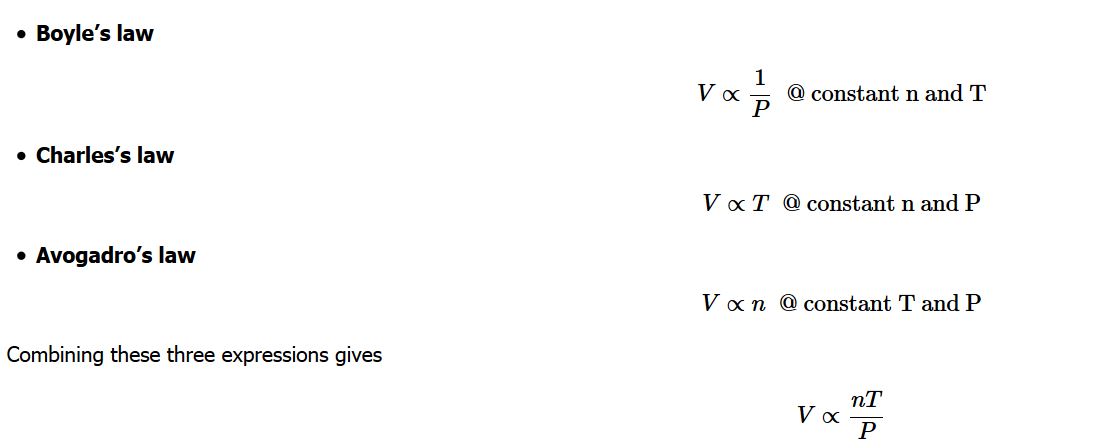
Combining these three expressions gives
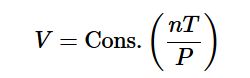
which shows that the volume of a gas is proportional to the number of moles and the temperature and inversely proportional to the pressure. This expression can also be written as:

Clearing the fractions by multiplying both sides of Equation below by P gives
PV=nRT
This equation is known as the ideal gas law.
An ideal gas is defined as a hypothetical gaseous substance whose behavior is independent of attractive and repulsive forces and can be completely described by the ideal gas law. In reality, there is no such thing as an ideal gas, but an ideal gas is a useful conceptual model that allows us to understand how gases respond to changing conditions. As we shall see, under many conditions, most real gases exhibit behavior that closely approximates that of an ideal gas. The ideal gas law can therefore be used to predict the behavior of real gases under most conditions. The ideal gas law does not work well at very low temperatures or very high pressures, where deviations from ideal behavior are most commonly observed.
Before we can use the ideal gas law, however, we need to know the value of the gas constant R. Its form depends on the units used for the other quantities in the expression. If V is expressed in liters (L), P in atmospheres (atm), T in kelvins (K), and n in moles (mol), then

 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















