
Uses & Application
 المؤلف:
........
المؤلف:
........
 المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
 الجزء والصفحة:
.......
الجزء والصفحة:
.......
 9-10-2018
9-10-2018
 1233
1233
Uses & Application
The vast majority of hydrogen produced industrially today is made either from treatment of methane gas with steam or in the production of "water gas" from the reaction of coal with steam. Most of this hydrogen is used in the Haber process to manufacture ammonia.
Hydrogen is also used for hydrogenation vegetable oils, turning them into margarine and shortening, and some is used for liquid rocket fuel. Liquid hydrogen (combined with liquid oxygen) is a major component of rocket fuel (as mentioned above combination of hydrogen and oxygen relapses a huge amount of energy). Because hydrogen is a good reducing agent, it is used to produce metals like iron, copper, nickel, and cobalt from their ores.
Because one cubic feet of hydrogen can lift about 0.07 lbs, hydrogen lifted airships or Zeppelins became very common in the early 1900s.However, the use of hydrogen for this purpose was largely discontinued around World War II after the explosion of The Hindenburg; this prompted greater use of inert helium, rather than flammable hydrogen for air travel.
Recently, due to the fear of fossil fuels running out, extensive research is being done on hydrogen as a source of energy.Because of their moderately high energy densities liquid hydrogen and compressed hydrogen gas are possible fuels for the future.A huge advantage in using them is that their combustion only produces water (it burns “clean”). However, it is very costly, and not economically feasible with current technology.
Combustion of fuel produces energy that can be converted into electrical energy when energy in the steam turns a turbine to drive a generator. However, this is not very efficient because a great deal of energy is lost as heat. The production of electricity using voltaic cell can yield more electricity (a form of usable energy). Voltaic cells that transform chemical energy in fuels (like H2 and CH4) are called fuel cells. These are not self-contained and so are not considered batteries. The hydrogen cell is a type of fuel cell involving the reaction between H2(g) with O2(g) to form liquid water; this cell is twice as efficient as the best internal combustion engine. In the cell (in basic conditions), the oxygen is reduced at the cathode, while the hydrogen is oxidized at the anode.
Reduction: O2(g)+2H2O(l)+4e- → 4OH-(aq)
Oxidation: H2(g) + 2OH-(aq) → 2H2O(l) + 2e-
Overall: 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
E°cell= Reduction- Oxidation= E°O2/OH- - E°H2O/H2 = 0.401V – (-0.828V) = +1.23
However, this technology is far from being used in everyday life due to its great costs.
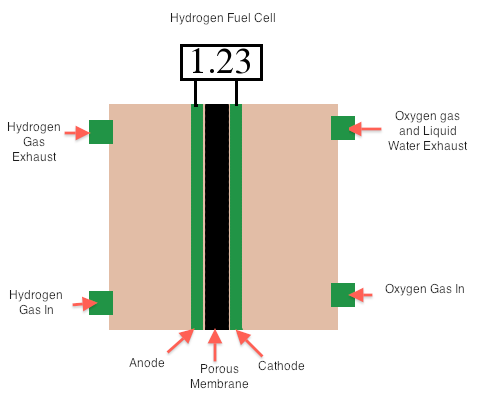
Image of A Hydrogen Fuel Cell. (Image made by Ridhi Sachdev)
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


