


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 5-9-2017
Date: 13-8-2017
Date: 23-11-2015
|
CHLORINATION OF BENZENE
Chlorination of benzene is an electrophilic substitution reaction in which Cl+ serves as the electrophile. The reaction occurs in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst such as FeCl3. The products are a mixture of mono- and dichlorobenzenes. The ortho- and the para-dichlorobenzenes are more common than meta-dichlorobenzene. The ratio of the monochloro to dichloro products essentially depends on the benzene/chlorine ratio and the residence time. The ratio of the dichloro-isomers (o- to p- to m-dichlorobenzenes) mainly depends on the reaction temperature and residence time:

Continuous chlorination processes permit the removal of monochlorobenzene as it is formed, resulting in lower yields of higher chlorinated benzene.
Monochlorobenzene is also produced in a vapor-phase process at approximately 300°C. The by-product HCl goes into a regenerative oxychlorination reactor. The catalyst is a promoted copper oxide on a silica carrier:
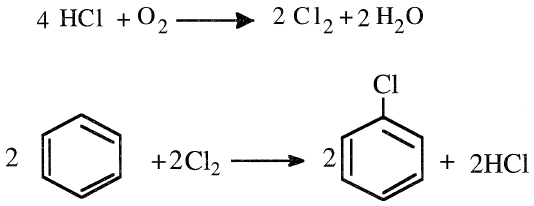
Higher conversions have been reported when temperatures of 234–315°C and pressures of 40–80 psi are used. Monochlorobenzene is the starting material for many compounds, including phenol and aniline. Others, such as DDT, chloronitrobenzenes, polychlorobenzenes, and biphenyl, do not have as high a demand for monochlorobenzene as aniline and phenol.



|
|
|
|
مخاطر خفية لمكون شائع في مشروبات الطاقة والمكملات الغذائية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"آبل" تشغّل نظامها الجديد للذكاء الاصطناعي على أجهزتها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلميّ يُواصل عقد جلسات تعليميّة في فنون الإقراء لطلبة العلوم الدينيّة في النجف الأشرف
|
|
|