


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 10-9-2016
Date: 3-9-2016
Date: 30-8-2016
|
Ferromagnetism
The spins of a regular Ising lattice interact by the energy
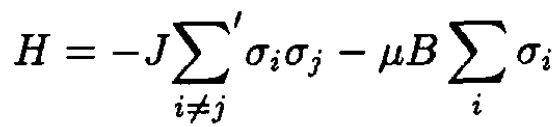 (i)
(i)
where B is an external field, μ is the magnetic moment, and the prime indicates that the summation is only over the nearest neighbors. Each spin σi has z nearest neighbors. The spins are restricted to equal ±1. The coupling constant J is positive. Following Weiss, represent the effect on σi of the spin–spin interaction in (i) by the mean field set up by the neighboring spins σj. Calculate the linear spin susceptibility χ(τ) using this mean field approximation. Your expression should diverge at some temperature τ = τc. What is the physical significance of this divergence? What is happening to the spin lattice at τ = τc?
SOLUTION
Using the mean field approximation, we may write the magnetization M of the lattice as
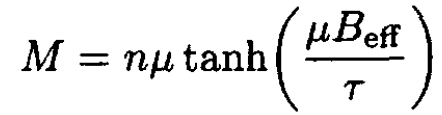 (1)
(1)
where n is the density of the spins and Beff is the sum of the imposed field and the field at spin σi produced by the neighboring spins:
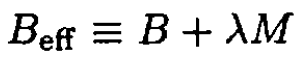 (2)
(2)
where λ is a constant. We may rewrite (1) as
 (3)
(3)
The susceptibility χ is given by
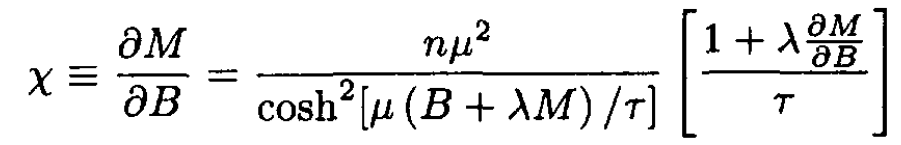 (4)
(4)
For B and M small we may rearrange (4), yielding
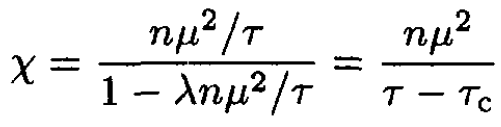 (5)
(5)
where τc ≡ λnμ2. The divergence of χ at τ = τc indicates the onset of ferromagnetism. The spins will align spontaneously in the absence of an applied magnetic field at this temperature.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تستعد لإطلاق الحفل المركزي لتخرج طلبة الجامعات العراقية
|
|
|