


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 29-8-2016
Date: 3-9-2016
Date: 11-8-2016
|
Attractive Delta Function Potential I
A particle of mass m moves in one dimension under the influence of an attractive delta function potential at the origin. The Schrodinger equation is
 (i)
(i)

Figure 1.1
a) Find the eigenvalue and eigenfunction of the bound state.
b) If the system is in the bound state and the strength of the potential is changed suddenly C → C', what is the probability that the particle remains bound?
SOLUTION
a) The bound state is stationary in time: its eigenvalue is E (E < 0), and the time dependence of the wave function is Ψ(x, t) = ѱ(x) exp(-iEt/h). The equation for the bound state is
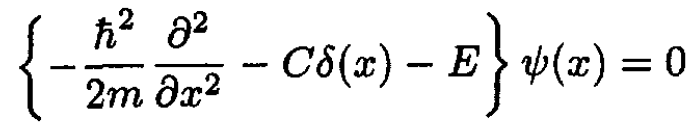 (1)
(1)
The bound state for x ≠ 0 has the form
 (2)
(2)
We have already imposed the constraint that ѱ(x) be continuous at x = 0. This form satisfies the requirement that ѱ(x) is continuous at the origin and vanishes at infinity. Away from the origin the potential is zero, and the Schrodinger equation just gives E = -h2α2/2m. A relation between C and E is found by matching the derivatives of the wave functions at x = 0. Taking the integral of (1) between 0+ and 0- gives
 (3)
(3)
Applying (3) to (2) gives the relations
 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
We have found the eigenvalue for the bound state. Note that the dimensions of C are energy × distance, which makes the eigenvalue have units of energy. Finally, we find the normalization coefficient A:
 (7)
(7)
b) When the potential constant changes from C → C', the eigenfunction changes from ѱ(x) → ѱ'(x), where the prime denotes the eigenfunction with the potential strength C'. In the sudden approximation the probability P0 that the particle remains in the bound state is given by
 (8)
(8)
where
 (9)
(9)
Substituting (2) into (9) and using the result of (7), we obtain
 (10)
(10)
Finally, using (5) yields
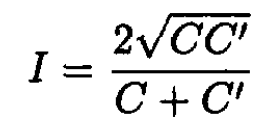 (11)
(11)
 (12)
(12)
It is easy to show that P0 ≤ 1 as required by particle conservation. If C = C', then P0 = 1 since there is no change, and the particle must stay in the bound state.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|