


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 18-1-2016
Date: 8-10-2017
Date: 9-10-2017
|
THE HYDROXYLATION OF AROMATIC RINGS
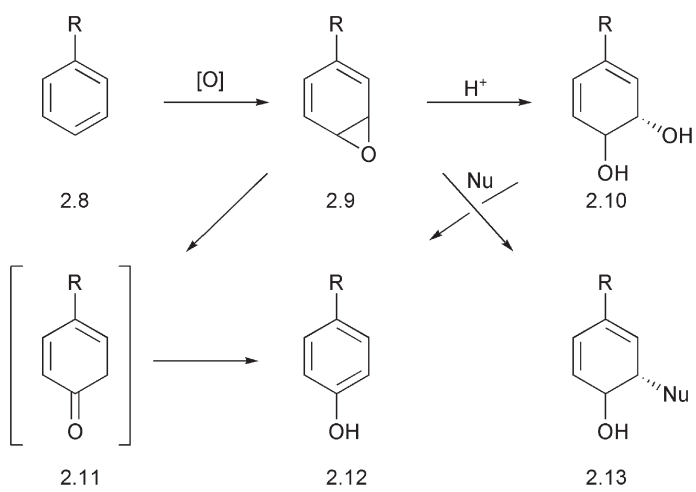
Many drugs contain an aromatic ring 2.8. Oxidation of the aromatic ring by the cytochrome P450s leads to the formation of a highly reactive, strained arene oxide 2.9. In the presence of acid, the epoxide undergoes hydrolysis to a diol 2.10, which may then be dehydrated to generate the aromatic ring of a phenol 2.12. Alternatively, a rearrangement may occur with the formation of a ketone 2.11 and thence by enolization, a phenol 2.12. The rearrangement of a hydrogen atom implicit in this process is known as the NIH shift after the National Institute of Health (USA) where it was discovered. The nucleophile in the cleavage of the epoxide may be the nitrogen of a nucleic acid base or the side chain amino group of a protein. The effect of this new bond is to attach the drug to the nucleic acid 2.13 or protein. This can lead to liver damage (hepatotoxicity). The nucleophile may also be the thiol of glutathione 2.4. This can lead to deactivation of a toxic metabolite.
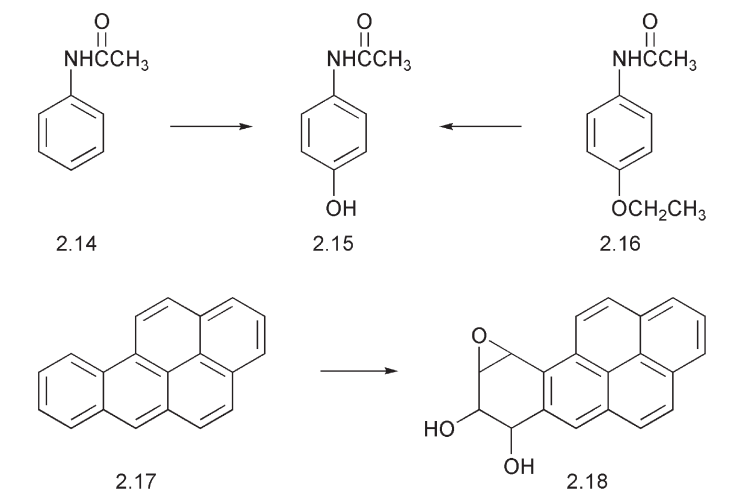
There are many examples of this step. Acetanilide 2.14 is a weak painkiller (analgesic), but it is converted by the liver to paracetamol 2.15, a more powerful analgesic. This is an example of a pro-drug:drug relationship. The aromatic hydrocarbon, benzopyrene 2.17 is converted to the carcinogenic 3,4-epoxy-7,8-dihydroxybenzopyrene 2.18.
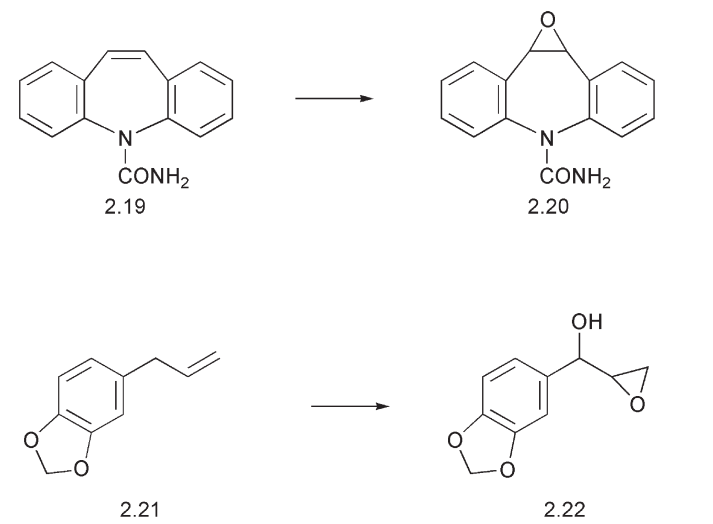
Nucleic acid bases such as guanosine react with the epoxide ring in 2.18. The aromatic ring of phenobarbital 2.6 may be hydroxylated. The benzylic position adjacent to an aromatic ring is also hydroxylated quite easily. An alkene may be epoxidized by the same process as exemplified by the metabolism of the tricyclic anti-depressant carbamazapine 2.19 to the epoxide 2.20. A combination of benzylic hydroxylation and epoxidation can be found in the metabolism of safrole 2.21 to the toxic hydroxy epoxide 2.22.



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي للقرآن الكريم يقيم جلسة حوارية لطلبة جامعة الكوفة
|
|
|