


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 16-2-2017
Date: 16-2-2017
Date: 16-2-2017
|
In 1883 Ehrlich introduced the diazo reaction for the detection of bilirubin. In 1913 Van den Bergh and Snapper applied the diazo reaction to serum after deproteinization. In 1916 Van den Bergh and Muller discovered the direct and indirect reading of bilirubin in serum. In 1937 Malloy and Evelyn adapted the bilirubin procedure to the photoelectric colorimeter. The Biotron Diagnostics Total Bilirubin method uses DMSO based on modification of Walters and Gerard. The method is sensitive, accurate and easy to perform. It compares very favorably with Malloy and Evelyn and Jendrassik and Grot.
TEST PRINCIPLE
Sulfanilic acid reacts with sodium nitrite to produce diazotized sulfanilic acid (diazo). Direct and indirect bilirubin couple with diazo to produce azobilirubin in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The intensity of the color produced is directly proportional to the amount of total bilirubin concentration present in the sample (at 546 nm.)
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
Total serum bilirubin is elevated in cases of obstructive jaundice, hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Elevations will occur when there is excessive destruction of hemoglobin.
SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND HANDLING
PATIENT PREPARATION
No special patient preparation is required.
SPECIMEN COLLECTION.
Fresh, clear, fasting serum is the preferred specimen.
Fasting avoids lipemic interference. Hemolyzed samples may produce falsely low values.
Use a standard venipuncture tube to draw patient sample.
The amount of sample required will depend on the analyzer used. The amount of serum required is in the range of 5-200 µl. Call Biotron's technical service department at 1-800-595 8766 for the recommended sample volume for your analyzer.
Record the patient's name, date and time of sample collection and preparation.
**SPECIMEN STORAGE
Specimens must be stored away from direct light as bilirubin is subject to photo-degradation. Serum samples may be stored for 2 hours at room temperature, 12 hours when refrigerated and 3 months when frozen. (10.10) Frozen samples should be thawed at room temperature and mixed completely before analysis. Thawed samples should not be refrozen.
It is recommended that testing be done as soon as possible after sample collection and preparation. If testing cannot occur immediately, store the sample properly using the guidelines above.
Reagent:
1. Diazo reagent:
To prepare diazo reagent mix 10 ml of solution (a) + 0.25 ml of solution (b)
2. Alkaline tartarate solution:
100 g NaOH + 350g Na,K,-tartarate /L
3. Ascorbic acid solution (40 g/L):
Dissolve 40 g in 1 L DW
4. Dyphylline reagent:
Dissolve 50 g in water at 40 °C and 125 g sodium acetate trihydrate.
Add 1g EDTA, cool and make to 1 L with DW.
5. Standard bilirubin solution, 200 mM
Technique:
Dilute the serum 1:5 with water. To each of three test tubes add the reagents in the order given, mixing well after each addition.
|
Sample |
Blank |
|
1.0 ml diluted serum |
1.0 ml DW |
|
0.5 ml diazo reagent |
0.5 ml diazo reagent |
|
2.0 ml dyphylline |
2.0 ml dyphylline |
|
Wait for 10 min |
|
|
0.1 ml ascorbic acid |
0.1 ml ascorbic acid |
|
1.5 ml alkaline tartarate |
1.5 ml alkaline tartarate |
|
Read immediately at 600 nm against water |
|
|
Dilute the standard 1:5 with water and determine the total bilirubin |
|
Calculation:
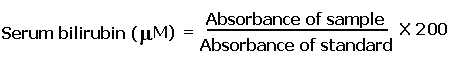



|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
عوائل الشهداء: العتبة العباسية المقدسة سبّاقة في استذكار شهداء العراق عبر فعالياتها وأنشطتها المختلفة
|
|
|