


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 4-5-2016
Date: 7-12-2015
Date: 2-6-2021
|
Active-Site Titrants
For determination of values for the kinetic rate constants and ligand-binding stoichiometries associated with an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, it is necessary to know the concentration of functional active sites of the enzyme. The latter value cannot be calculated simply from the total concentration of protein and molecular weight of the enzyme; even when the enzyme preparation has been shown to be homogeneous by a variety of techniques, it is possible that inactive enzyme is present. The inactivity could be due to the inability of the enzyme to bind substrate or perform the chemistry of the reaction, or both. Therefore, before undertaking detailed kinetic investigations on any enzyme, it is important to determine the concentrations of the active sites that can both bind the ligands and are active.
The concentration of binding sites can be obtained from data for the reversible inhibition of an enzyme by a tight-binding substrate analogue that gives rise to competitive inhibition. Tight-binding inhibition occurs under conditions where the total inhibitor concentration It is comparable to the total enzyme concentration Et, and a substantial fraction of the inhibitor is bound, so that allowance has to be made for the reduction of free inhibitor concentration as a result of formation of the enzyme-inhibitor complex (1). The variation of the steady-state velocity as a function of the concentrations of It and Et is described by Equation 1:

where k denotes the maximum rate of product formation in terms of moles per mole of enzyme per second, Ka is the Michaelis constant for the substrate present at concentration A, and represents an apparent inhibition constant whose relationship to the true inhibition constant Ki for the interaction of I with E is given by
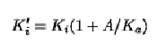
Equation 1 also applies to multisubstrate reactions, provided that the nonvaried substrates are present at saturating concentrations. When no assumptions are made about the purity of the enzyme, Et of Equation 1 is replaced by aEx, where a represents the degree of purity of the enzyme and Ex denotes the total protein concentration. Fitting to the modified form of Equation 1 of steady-state velocity data obtained at varying concentrations of It and Et would yield values for as well as a, which would yield a measure of the concentration of binding sites (2, 3).
The technique of active-site titration is used to determine the concentration of catalytically active enzyme (4, 5). It requires that on mixing enzyme and the titrating substrate, there is an initial rapid burst of product formation because of the accumulation of an enzyme-bound intermediate whose rate of breakdown is much slower than its rate of formation. The procedure can be illustrated by reference to the Uni–Bi reaction:

for which P is released before Q, and at a very much faster rate. Specific measurement of the release of P as a function of time would yield a plot (Fig. 1) that consists of curved (burst) and linear sections. The intersection of the extrapolated linear curve with the vertical ordinate would give the concentration of P that is equal to the concentration of functional active sites.
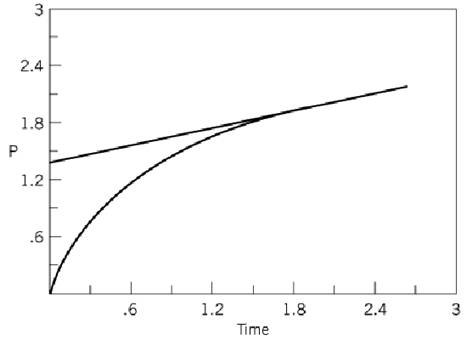
Figure 1. Active-site titration curve showing burst formation of a covalent enzyme-intermediate complex.
Active-site titrations may be performed with chromogenic or radioactive substrates, and rapid reaction techniques are often required. This is not the case, however, for determination of the active-site concentration of hexokinase (6). This can be done by incubating the enzyme with 14C-glucose and ATP complexed with Cr3+, rather than the usual Mg2+, and separating the enzyme-CrADP-glucose-6-phosphate complex on a Sepharose column. In this case, the enzyme undergoes only a single turnover, and the product complex has a half-life of over 10 min, so the amount of 14C associated with the enzyme gives a measure of the active-site concentration (6).
Comparison of the results obtained from tight-binding inhibition and active-site titration studies could yield information about the presence in an enzyme preparation of substantial proportion of sites that can bind substrate, but cannot catalyze the reaction.
References
1. J. W. Williams and J. F. Morrison (1979) Meth. Enzymol. 63, 437–467.
2. J. F. Morrison and S. R. Stone (1985) Comments Mol. Cell. Biophys. 2, 347–368.
3. M. J. Sculley and J. F. Morrison (1986) Biochem. Biophys. Acta 874, 44–53.
4. A. Fersht (1977) Enzyme Structure and Mechanism, W. H. Freeman and Company, San Francisco, Calif., pp. 122–126.
5. F. J. Kezdy and E. T. Kaiser (1970) Meth. Enzymol. 19, 3–20.
6. K. D. Danenberg and W. W. Cleland (1975) Biochemistry 14, 28–39.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تستعد لإطلاق الحفل المركزي لتخرج طلبة الجامعات العراقية
|
|
|