


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 17-11-2015
Date: 17-11-2015
Date: 17-11-2015
|
Study of fungi
Specimens are studied in one of the two ways: those that cannot be grown under artificial conditions are studied directly, and those that must or can be cultured or isolated are studied indirectly.
1-Indirect study:
Many pathogens in plant material, soil and water must first be isolated and obtained in pure culture before they can be studied. These fungi are usually not visible to the unaided eye, although the disease symptoms often are.
Isolation of fungi
Isolation from soil:
Dilution method:
In this technique 1 gram (dry weight) of the SOIL to be studied is ground up (if necessary) and dispersed in 9 ml of sterile water. One milliliter of this solution is transferred to a second tube containing 9 ml of sterile water, resulting in a 0.01 dilution of the spore mass in the original material. The process is repeated to yield dilutions of 0.001, 0.0001, and 0.00001 or even further if necessary. A 1-ml portion from each dilution is pipetted to a separate Petri dish, and cooled, melted agar medium poured over it. The plate should be moved gently on the table in a figure-of-eight motion to effect proper dispersion. Alternatively, the solution can be put on the surface of solidified medium and spread evenly throughout.
After a few days' incubation, colonies will appear in varying densities, depending upon the amount of dilution from the original material. The number of spores present in the original sample can be calculated roughly by selecting the plates showing 40-100 colonies and writing down the colony count. With this information the following calculation can be performed:
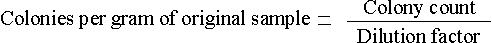
The accuracy of this technique is low when only one plate is counted. There are numerous contributing factors, including improper dispersion of spores during dilution, failure to break up spore masses, or mutual inhibition of growth by certain fungi. Greater accuracy is attained by doing several plates at the most desirable dilution. This technique allow scientists to compare one soil with another on a statistical basis.
Direct method:
It is a simple technique, requiring the placing of small bits of the soil (0.005-0.015) on the surface of the agar or the pouring of melted but cooled agar over the fragments .the particles are dispersed throughout the medium by rotating the dish. After a few days' incubation mould colonies appear on the surface, and can be transferred into pure culture.



|
|
|
|
مخاطر خفية لمكون شائع في مشروبات الطاقة والمكملات الغذائية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"آبل" تشغّل نظامها الجديد للذكاء الاصطناعي على أجهزتها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلميّ يُواصل عقد جلسات تعليميّة في فنون الإقراء لطلبة العلوم الدينيّة في النجف الأشرف
|
|
|