


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 12-8-2020
Date: 10-6-2019
Date: 10-6-2019
|
One definition of energy is the capacity to do work. The easiest form of work to visualize is mechanical work (Figure 1.1), which is the energy required to move an object a distance d when opposed by a force F, such as gravity:
work = force x distance
Because the force (F) that opposes the action is equal to the mass (m) of the object times its acceleration (a), we can also write Equation above as follows:
work= mass x acceleration x distance
Recall from that weight is a force caused by the gravitational attraction between two masses, such as you and Earth.
Consider the mechanical work required for you to travel from the first floor of a building to the second. Whether you take an elevator or an escalator, trudge upstairs, or leap up the stairs two at a time, energy is expended to overcome the force of gravity. The amount of work done (w) and thus the energy required depends on three things:
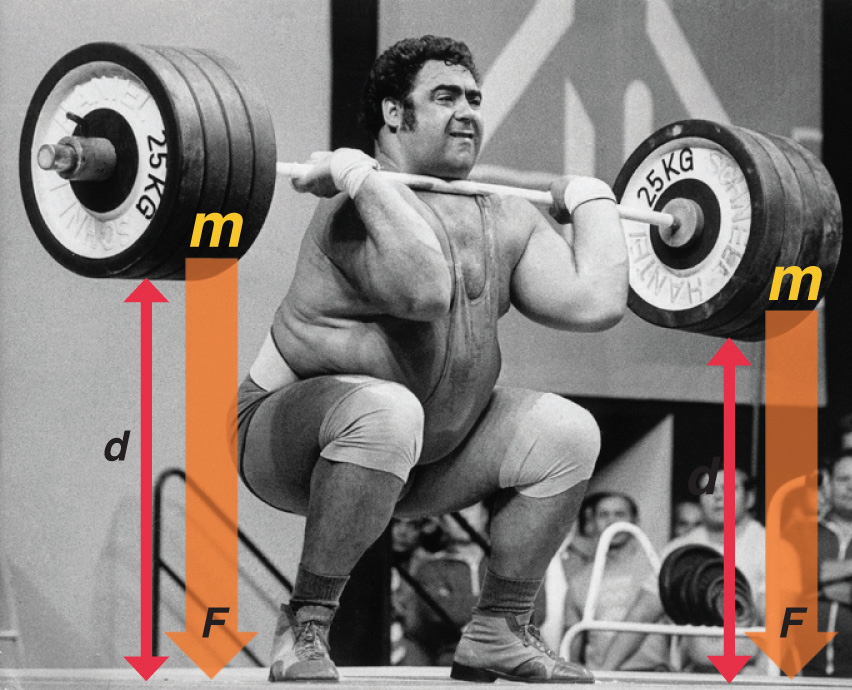
Figure 1.1 : An Example of Mechanical Work. One form of energy is mechanical work, the energy required to move an object of mass m a distance d when opposed by a force F, such as gravity.
In contrast, heat (q) is thermal energy that can be transferred from an object at one temperature to an object at another temperature. The net transfer of thermal energy stops when the two objects reach the same temperature.
Energy is an extensive property of matter—for example, the amount of thermal energy in an object is proportional to both its mass and its temperature. A water heater that holds 150 L of water at 50°C contains much more thermal energy than does a 1 L pan of water at 50°C. Similarly, a bomb contains much more chemical energy than does a firecracker. We now present a more detailed description of kinetic and potential energy.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|