


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 30-10-2020
Date: 17-4-2019
Date: 24-4-2019
|
Impurities can be classified as interstitial or substitutional. An interstitial impurityA point defect that results when an impurity atom occupies an octahedral hole or a tetrahedral hole in the lattice between atoms. is usually a smaller atom (typically about 45% smaller than the host) that can fit into the octahedral or tetrahedral holes in the metal lattice (Figure 1.1).
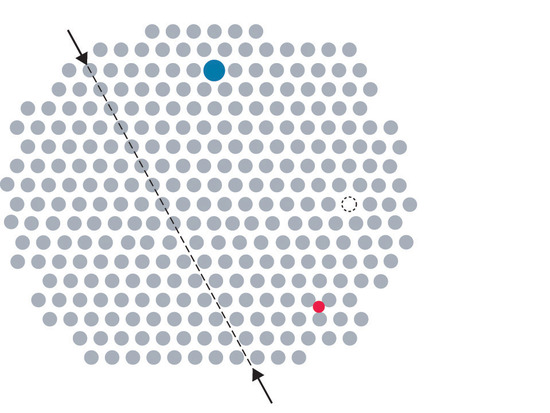
Figure 1.1 Common Defects in Crystals
Steels consist of iron with carbon atoms added as interstitial impurities (Table 1.1 ). The inclusion of one or more transition metals or semimetals can improve the corrosion resistance of steel.
Table 1.1 Compositions, Properties, and Uses of Some Types of Steel
| Name of Steel | Typical Composition* | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| low-carbon | <0.15% C | soft and ductile | wire |
| mild carbon | 0.15%–0.25% C | malleable and ductile | cables, chains, and nails |
| high-carbon | 0.60%–1.5% C | hard and brittle | knives, cutting tools, drill bits, and springs |
| stainless | 15%–20% Cr, 1%–5% Mn, 5%–10% Ni, 1%–3% Si, 1% C, 0.05% P | corrosion resistant | cutlery, instruments, and marine fittings |
| invar | 36% Ni | low coefficient of thermal expansion | measuring tapes and meter sticks |
| manganese | 10%–20% Mn | hard and wear resistant | armor plate, safes, and rails |
| high-speed | 14%–20% W | retains hardness at high temperatures | high-speed cutting tools |
| silicon | 1%–5% Si | hard, strong, and highly magnetic | magnets in electric motors and transformers |
| *In addition to enough iron to bring the total percentage up to 100%, most steels contain small amounts of carbon (0.5%–1.5%) and manganese (<2%). | |||
In contrast, a substitutional impurityA point defect that results when an impurity atom occupies a normal lattice site. is a different atom of about the same size that simply replaces one of the atoms that compose the host lattice . Substitutional impurities are usually chemically similar to the substance that constitutes the bulk of the sample, and they generally have atomic radii that are within about 15% of the radius of the host. For example, strontium and calcium are chemically similar and have similar radii, and as a result, strontium is a common impurity in crystalline calcium, with the Sr atoms randomly occupying sites normally occupied by Ca.



|
|
|
|
مخاطر خفية لمكون شائع في مشروبات الطاقة والمكملات الغذائية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"آبل" تشغّل نظامها الجديد للذكاء الاصطناعي على أجهزتها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تستخدم لأول مرة... مستشفى الإمام زين العابدين (ع) التابع للعتبة الحسينية يعتمد تقنيات حديثة في تثبيت الكسور المعقدة
|
|
|