


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 12-7-2018
Date: 14-11-2019
Date: 1-9-2019
|
Reduction of aldehydes and ketones to alcohols is most commonly carried out by metal hydride reagents, dissolving metal reagents, and sometimes by catalytic hydrogenation. A table listing these reagents and the conditions under which they are best used as show in below.
| Reagent | Preferred Solvents | Functions Reduced | Reaction Work-up |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium Borohydride NaBH4 |
ethanol; aqueous ethanol 15% NaOH; diglyme avoid strong acids |
aldehydes to 1º-alcohols ketones to 2º-alcohols 1,2-reduction of enones is favored by CeCl3 inert to most other functions |
1) simple neutralization 2) extraction of product |
| Lithium Aluminum Hydride (LAH) LiAlH4 |
ether; THF avoid alcohols and amines avoid halogenated compounds avoid strong acids |
aldehydes to 1º-alcohols ketones to 2º-alcohols carboxylic acids to 1º-alcohols esters to alcohols epoxides to alcohols nitriles & amides to amines halides & tosylates to alkanes most functions react |
1) careful addition of water 2) dissolve aluminum salts 3) extraction of product |
| Lithium tri t-Butoxyaluminohydride LiAlH(Ot-C4H9)3 |
ether; THF avoid alcohols and amines avoid halogenated compounds avoid strong acids |
fast: acid chlorides to aldehydes (at -78 ºC) 3º-amides to aldehydes (at -78 ºC) nitriles to aldehydes (at -78 ºC) slower: aldehydes to 1º-alcohols ketones to 2º-alcohols |
1) careful addition of water 2) dissolve aluminum salts 3) extraction of product |
| Diisobutylaluminum Hydride AlH[CH2CH(CH3)2]2 |
THF; toluene avoid alcohols and amines avoid halogenated compounds avoid strong acids |
fast: acid chlorides to aldehydes (at -78 ºC) 3º-amides to aldehydes (at -78 ºC) nitriles to aldehydes (at -78 ºC) slower: aldehydes to 1º-alcohols ketones to 2º-alcohols |
1) careful addition of water 2) dissolve aluminum salts 3) extraction of product |
| Diborane B2H6 = 2 BH3 |
ether; THF sulfide complex in CH2Cl2 complexes with amines avoid alkenes & alkynes |
carboxylic acids to 1º-alcohols aldehydes to 1º-alcohols ketones to 2º-alcohols nitriles to amines esters & epoxides slowly reduced |
1) dilute acid or H2O2 2) extraction of product |
|
Hydrogen & Catalyst Modified (poisoned) Catalyst |
alcohols, ethers, hydrocarbons or carboxylic acids |
alkenes & alkynes to alkanes (fast) alkynes to alkenes |
filter to remove catalyst |
|
Reactive Metals Mg or Al or Zn or Fe |
liq. ammonia & ether co-solvents water, alcohols, acetic acid |
ketones to 2º-alcohols cleaves activated substituents |
1) quench with NH4Cl extract product from salts |
Prior to the development of these new and powerful reduction methods, the conversion of carbonyl compounds to alcohols was often effected by hydrogen transfer from an alkoxide salt. This procedure, known as the Meerwein-Pondorf-Verley reaction, is illustrated by the following equation and mechanism ( the hydride-like hydrogen is colored red). Aluminum isopropoxide has been the most common hydrogen source in most cases, but lanthanide salts, such as ROSmI2 have been used with good results. This reduction is specific for aldehyde and ketone carbonyl functions, so other easily reduced functions such as nitro groups and halogen are unaffected.

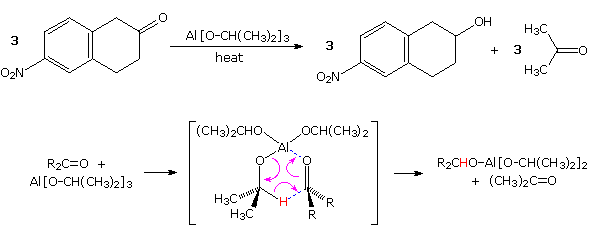
Not only are two hydrogens delivered independently from the least hindered (convex) side of the cis-decalin substrate in example 1, but the easily reduced double bond of the enedione remains unchanged. The initially formed cis-diol undergoes lactonization with the neighboring methyl ester. It should be noted that a similar reductive hydride transfer takes place when large alkyl Grignard reagents react with hindered ketones, as shown in equation 2.
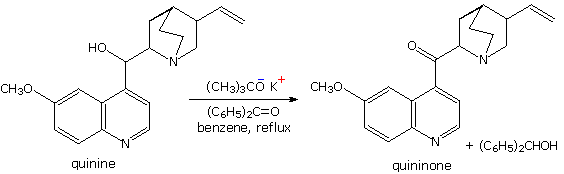
The MVP reduction is also an oxidation, as evidenced by the conversion of isopropoxide to acetone. Consequently, the reaction can be converted into an oxidation of alcohols to ketones or aldehydes. This procedure is called the Oppenauer oxidation. The reaction displayed below is an example of the Oppenauer oxidation in which benzophenone is the oxidant. Two significant features may be noted. First, the oxidation is specific for alcohols, and does not oxidize other sensitive functions such as amines and sulfides. Second, although aluminum or other coordinating metals are often used as cationic partners, alkali metals alone will suffice.



|
|
|
|
مخاطر خفية لمكون شائع في مشروبات الطاقة والمكملات الغذائية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"آبل" تشغّل نظامها الجديد للذكاء الاصطناعي على أجهزتها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تستخدم لأول مرة... مستشفى الإمام زين العابدين (ع) التابع للعتبة الحسينية يعتمد تقنيات حديثة في تثبيت الكسور المعقدة
|
|
|